AFP resurgence and histological lesions in late stages of chemical hepato-carcinogenesis and during hepatoma development
Wolf D. Kuhlmann
Laboratory Diagnostics & Cell Science, 56112 Lahnstein
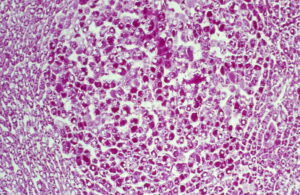
Liver with hepatocellular carcinoma, serial sections with immunostaing for AFP and EH (Epoxid-hydrolase) and PAS
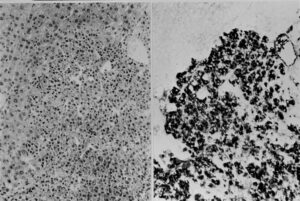
AFP in hepatocellular carcinoma. Detection of cellular AFP at low magnification (upper left), a serial tissue section was PAS stained (upper right).
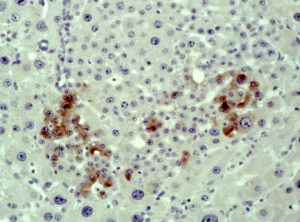
Below: higher magnification view from the border of the carcinoma nodule (left with HE staining; at the right side, serial section with AFP immunostaining). Neoplastic hepatocytes penetrate normal liver area, AFP expression is only detected in carcinoma cells.
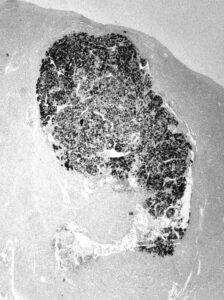
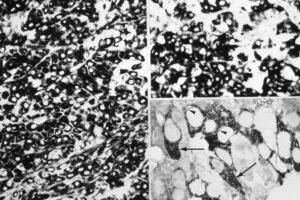
At the bottom, AFP positive carcinoma (left). 3H thymidine incorporation is detected in AFP positive carcinoma cells (arrows) while the adjacent normal part of the liver is not labelled
Serial sections of liver with hepatocellular carcinoma penetrating normal liver tissue. Left: HE stained section. Right: AFP immunostained section. Normal hepatocytes do not stain for AFP
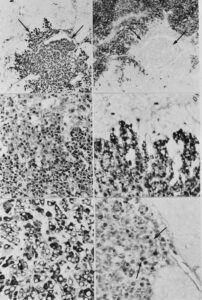
Detection of AFP in transplanted liver cancer cells. Above and left: tissue was fixed in ethanol/acetic acid, embedded in paraffin, then section was stained for AFP. Above and right: Tumor was fixed in formaldehyde/glutaraldehyde, dehydrated, embedded in paraffin, then tissue section was stained for AFP. Below, aldehyde fixed tissue was processed and prepared for AFP immunostaining, dehydrated and embedded in resin. Semithin sections were cut and viewed in the light microscope. Note AFP reaction in the cytoplasm of cancer cells (arrows)
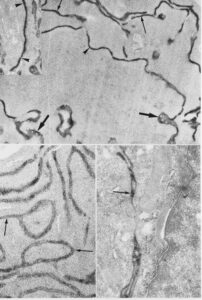
Hepatocellular carcinoma, formald./glutarald. fixation, thick frozen-cut sections were cut with a cryomicrotome and immunostained for AFP. These tissue sections were embedded in Epon resin. Then, ultrathin sections were prepared for electron microscopy. Note AFP in RER lamellae (arrow), PNS and Golgi apparatus (arrow head). Lower left: AFP in RER lamellae. Lower right: extracellular AFP between adjacent carcinoma cells