Lectins as specific ligands for the study of glycoconjugates in cell research and histopathology
Wolf D. Kuhlmann
Laboratory Diagnostics & Cell Science, 56112 Lahnstein
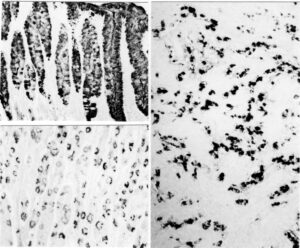
Lectin binding in duodenal mucosa. (1) Arachis hypogaea (PNA) positivity in Brunner’s glands. (2) Ulex europaeus (UEA I) positivity of striated columnar cells and the brush border. Occasional positive goblet cells and staining of Brunner’s glands. (3) UEA I positivity of Brunner’s glands and numerous goblet cells
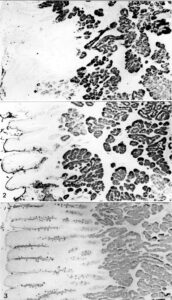
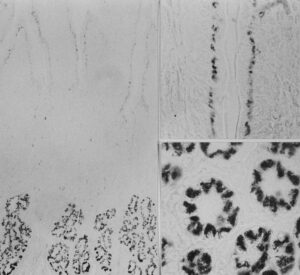
Lectin binding of Griffonia simplicifolia (GS) lectins: GS I lectin-binding in gastrointestinal mucosa; (1) GS I (A+B) lectin-binding of parietal cells, indirect peroxidase method; (2) GS I (B4) lectin-binding of parietal cells, indirect colloidal gold method; (3) GS I (A+B) binding of duodenal mucosa, indirect peroxidase labelling; note staining in Brunner’s glands and in supranuclear regions of enterocytes; Insets: GS I (B4) in enterocytes (left) and GS I (B4) in Brunner’s glands (right)
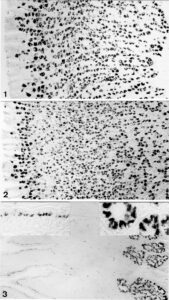
Lectin immunohistology: GS I (A+B) lectin-binding in gastrointestinal mucosa, indirect peroxidase staining. Left: Crypt of duodenal mucosa, positive reaction in some goblet cells and supranuclear regions of columnar cells. Right: Gastric mucosa, treated with periodic acid prior to lectin-staining, indirect peroxidase method; note positive reaction in mucus neck cells
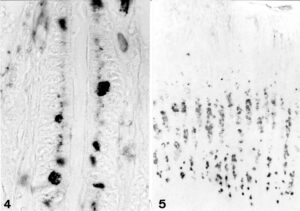
Lektin immunohistology: GS I (A+B) binding of duodenal mucosa, indirect peroxidase labelling. Left: note staining in Brunner’s glands and in supranuclear regions of enterocytes. Top right: GS I (B4) in supranuclear areas of columnar cells. Bottom right: high magnification view of GS I (B4) binding to Brunner’s gland cells