Reagents for immunohistology
Wolf D. Kuhlmann
Laboratory Diagnostics & Cell Science, 56112 Lahnstein
Typical and often used methods for the preparation of biomolecules such as antigens and antibodies for cell research. Details are described in IMMUNO ENZYME TECHNIQUES IN CYTOCHEMISTRY as well as in the Cell Science chapters of this Homepage.
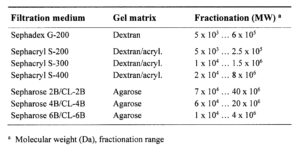
Principles of ion exchange chromatography, molecular sieving with gel filtration media and chromatofocusing. In the latter, the protein net charge determines its binding to the ion exchanger. In the course of chromatofocusing, a pH gradient from the column pH to eluant buffer pH is formed. The isoelectric point of the proteins and pH of the elution buffer determine protein migration.
Bioselective affinity chromatography is a most powerful separation technique. A biospecific ligand (f.e. antibody) is first attached to an insoluble matrix, and the molecules to be purified are selectively and reversibly absorbed to the immobilized ligand. Thus, antigens or antibodies may by coupled to agarose beads for the isolation of antibodies or antigens, respectively.
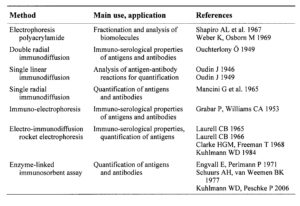
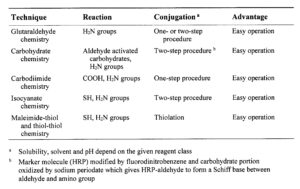
Table: Useful techniques to prepare antibody-enzyme conjugates
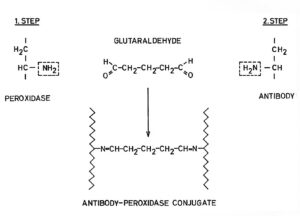
Two-step reaction method to prepare antibody-enzyme conjugates using glutaraldehyde as cross-linking reagent
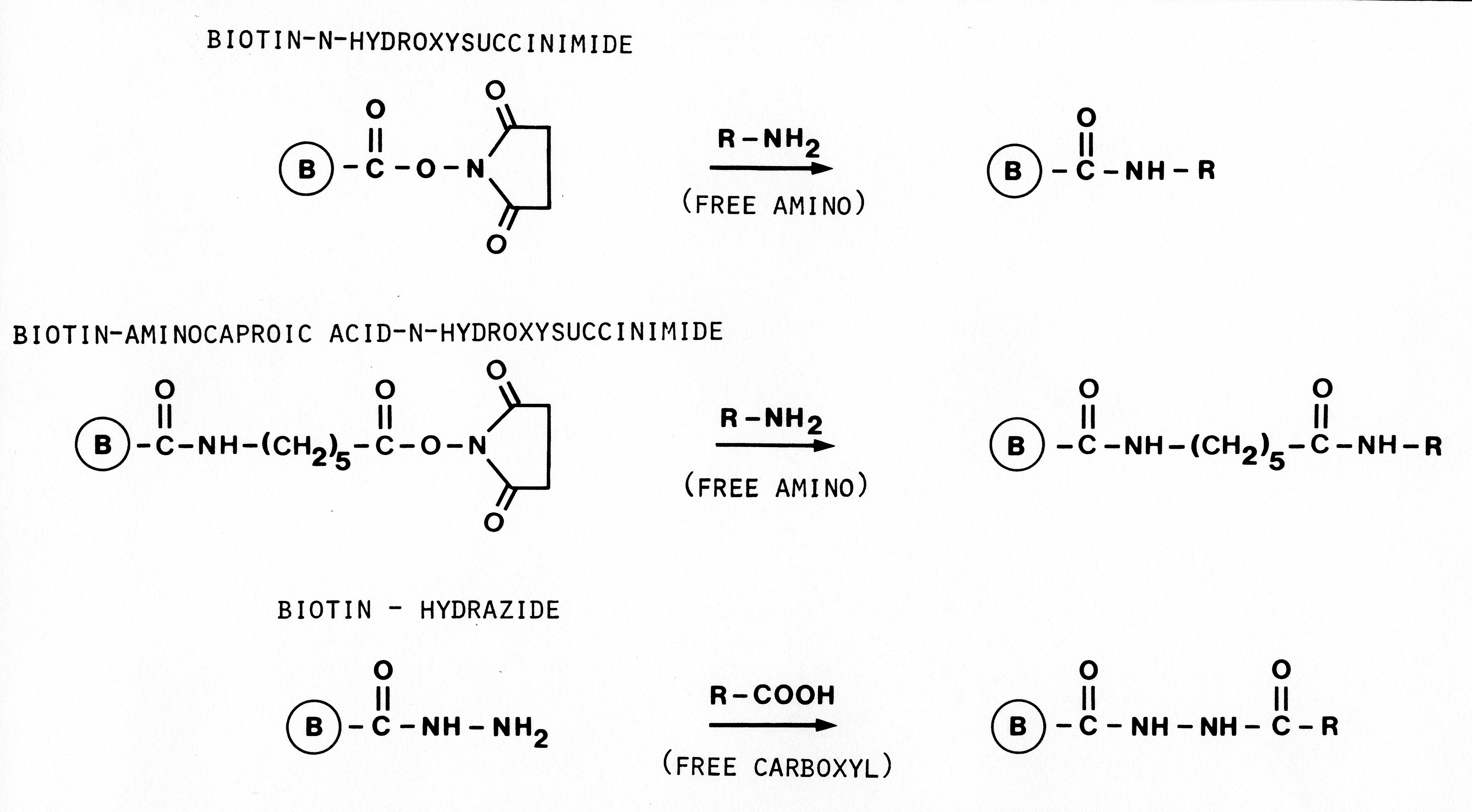
Reaction of proteins (R-NH2) via amino groups in the labeling procedure with biotin derivatives
Fractionation, purification of antibody-enzyme conjugates by gel filtration and affinity chromatography. High degree of purification in the case of HRP conjugates can be obtained with Concanavalin A affinity chromatography. Peroxidase conjugated antibodies are eluted from the affinity matix using alpha-methyl-D-mannoside
Selection of appropriate enzyme substrates in histochemistry and immuno-enzyme techniques