Principles and technical approaches for the detection of molecular staining in immunohistology or other ligand binding assays
Wolf D. Kuhlmann
Laboratory Diagnostics & Cell Science, 56112 Lahnstein
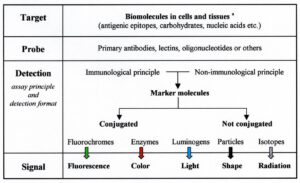
Molecular probe mapping: principles of qualitative and quantitative ligand assays. Generally, methods and procedures need adaptions to the study aim. Some popular approaches for immunohistology are here presented. The choice of a certain procedure is often a matter of experience and personal preference. Other and new developments can be expected
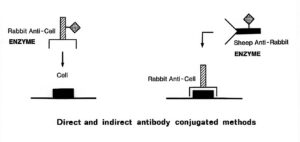
In the direct method, a specific antibody against the tissue antigen is prepared and coupled with a marker (e.g. peroxidase, HRP). In the indirect method, also termed „sandwich“ methods, antibodies from a species A against the tissue antigen are used in the first incubation step. Then, in the second step, antibodies from a species B against immunoglobulin of species A and conjugated with a marker molecule are employed
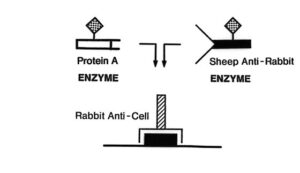
Several distinct indirect techniques are possible which make use of „binding and bridging“ methods such as Protein A, hybrid antibodies, Avidin-Biotin binding
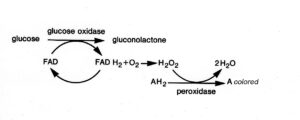
Two-step enzyme methods for immunostaining by co-immobilization of GOD and HRP molecules at the cellular sites is an alternative choice. The method relies on enzyme-amplification by a coupled enzyme substrate system where enzyme E1 (GOD) and enzyme E2 (HRP), are co-immobilized. Then, E1 catalyzes substrate P1 which in turn serves as substrate S2 for E2 to oxidize the added chromogen into an insoluble and colored product P2 (for example DAB)
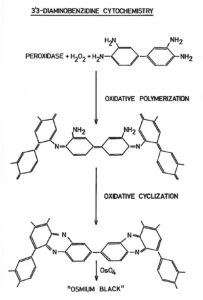
Peroxidase (HRP) diaminobenzidine (DAB) cytochemistry: peroxidase and H2O2 react by oxidative polymerization and cyclization of DAB which gives finally a colored and insoluble product
GOD-HRP coupled enzyme cytochemistry: the two-step enzyme technique of the coupled GOD-HRP staining method uses HRP as secondary system enzyme. GOD generates H2O2 by the oxidation of D-glucose. Then, H2O2 serves as substrate for HRP which oxidizes the chromogen AH2 to yield an insoluble colored product (Acolored)
In situ hybridization for the detection of nucleic acids using an enzyme labeled antibody technique. Alternatively, nucleic acids can be detected by Avidin-Biotin techniques with preformed ABC complexes